Bookkeeping
Relationship Between Variances, Disposing of Variances
NỘI DUNG TRANG
As a result of this unfavorable outcome information, the company may consider using cheaper materials, changing suppliers, or increasing prices to cover costs. To illustrate standard costs variance analysis for direct labor, refer to the data for NoTuggins in Exhibit 8-1 above. Each unit requires 0.25 direct labor hours at an average rate of $18 per hour for a total direct labor cost of $4.50 per unit.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
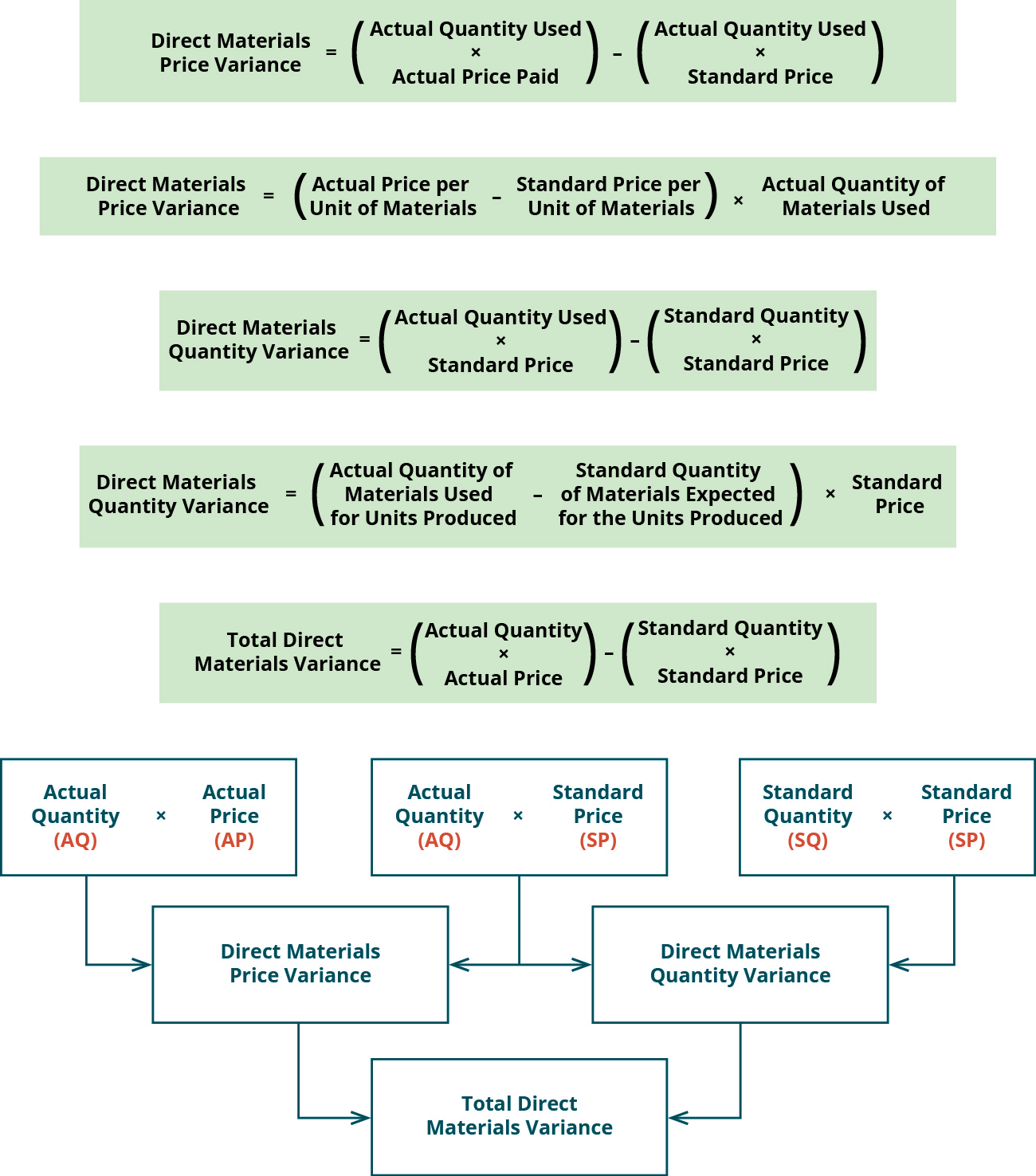
In this case, the actual price per unit of materials is \(\$6.00\), the standard price per unit of materials is \(\$7.00\), and the actual quantity used is \(0.25\) pounds. If the actual price paid per unit of material is lower than the standard price per unit, the variance will be a favorable variance. A favorable outcome means you spent less on the purchase of materials than you anticipated.
Step 4: Use the Formula – How is Efficiency Variance Calculated?
Connie’s Candy also wants to understand what overhead cost outcomes will be at 90% capacity and 110% capacity. The following information is the flexible budget Connie’s Candy prepared to show expected overhead at each capacity level. Knowledge of this variance may prompt a company’s management team to increase product prices, use substitute materials, or find other offsetting sources of cost reduction. Accounting professionals have a materiality guideline which allows a company to make an exception to an accounting principle if the amount in question is insignificant. The products in a manufacturer’s inventory that are completed and are awaiting to be sold. You might view this account as containing the cost of the products in the finished goods warehouse.
Step 1: Determine the Budgeted Quantity – How is Efficiency Variance Calculated?
If the calculation result is positive, then the efficiency variance is favorable because the actual quantity used is less than the budgeted quantity. If the result is negative, the efficiency variance is unfavorable because the actual quantity used is more than the budgeted quantity. Efficiency variance can increase costs, such as higher labor costs, materials waste, and increased energy consumption. Ignoring efficiency variance can lead to continued waste and inefficiencies, resulting in increased costs for the company. Inadequate maintenance can cause equipment to break down more frequently, leading to increased downtime and reduced efficiency. Failure to properly maintain equipment can also lead to lower quality output, resulting in increased costs due to the need for rework or the rejection of defective products.
If a company’s efficiency variance results in higher costs than anticipated, it may need to take action to address the issue. This could involve renegotiating supplier contracts to reduce material costs, streamlining production processes to reduce labor costs, or identifying ways to reduce overhead costs. The company can improve its profitability and competitiveness by addressing efficiency variance and reducing costs. The difference between the expected and actual cost incurred on purchasing direct materials, expressed as a positive or negative value, evaluated in terms of currency. This means that the actual direct materials used were less than the standard quantity of materials called for by the good output.
Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
The completed top section of the template contains all the numbers needed to compute the direct materials quantity and price variances. The direct materials quantity and price variances regressive vs proportional vs progressive taxes are used to determine if the overall variance is a quantity issue, price issue, or both. Standard costs are established for all direct materials used in the manufacturing process.
The ultimate motive behind their calculation is to control costs and enhance improvement. Angro Limited, a single product American company, employs a proper standard costing system. The normal wastage and inefficiencies are taken into account while setting direct materials price and quantity standards. Variances are calculated and reported at regular intervals to ensure the quick remedial actions against any unfavorable occurrence.
- Companies that lack the financial resources to invest in new equipment or training programs may find it challenging to address this issue effectively.
- The age and condition of current equipment are essential factors to consider.
- Standards for variable manufacturing costs include both quantity and price standards.
- Finally, efficiency variance can help companies to identify areas where they can reduce their environmental impact.
- The quality control manager works closely with the production manager to ensure that production processes are optimized and that efficiency variance is minimized.
This can help them meet sustainability goals, reduce their carbon footprint, and improve their reputation as socially responsible. One of the primary reasons why efficiency variance is vital in the manufacturing industry is that it can directly impact a company’s profitability. When a company can produce goods or services at a higher rate than expected, it can increase its revenue and improve its bottom line. Conversely, when a company is less efficient than expected, it may experience decreased revenue and increased costs, negatively impacting its profitability. The third step is to find the actual output achieved during the measuring period. This is the quantity of units produced or services rendered, as measured by the company’s production system or other tracking methods.
For example, let’s say that a company budgeted to produce 1,000 units during a measuring period, with a standard rate of $10 per unit. To calculate the efficiency variance, you would first calculate the quantity variance by subtracting the budgeted quantity (1,000) from the actual quantity (900), which gives you a variance of -100. To determine the overhead standard cost, companies prepare a flexible budget that gives estimated revenues and costs at varying levels of production. The standard overhead cost is usually expressed as the sum of its component parts, fixed and variable costs per unit. Note that at different levels of production, total fixed costs are the same, so the standard fixed cost per unit will change for each production level. However, the variable standard cost per unit is the same per unit for each level of production, but the total variable costs will change.